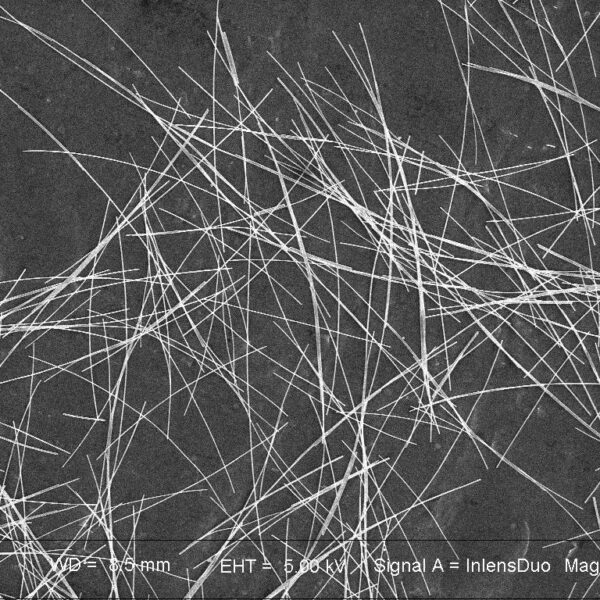
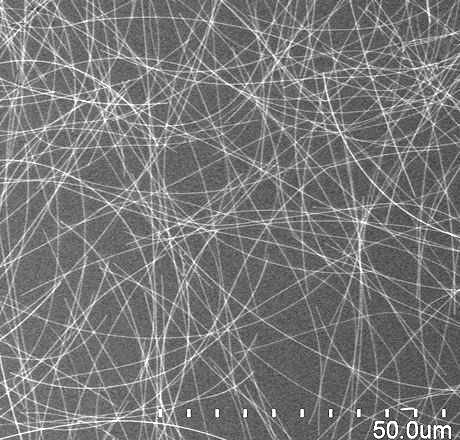
Description
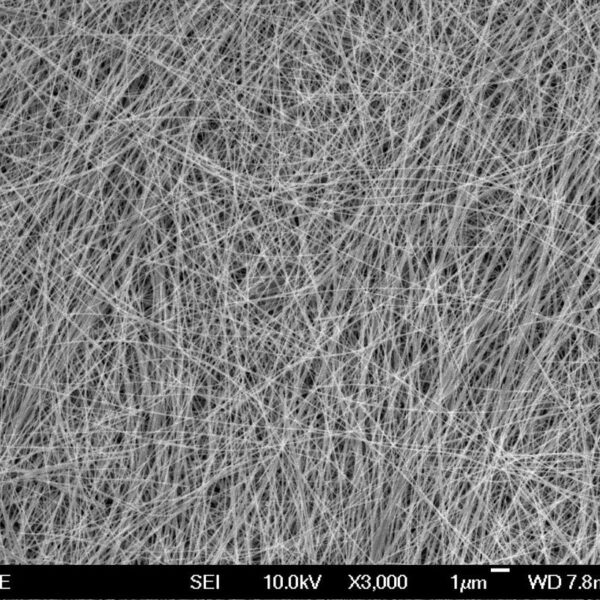
Novarials’ Silver Nanowire Ink for Screen Printing is a formulated ready-to-use water-based viscous liquid for creating high optical quality transparent conductive layers. The ready-to-use solution contains silver nanowires (~30nm in diameter), adhesives and other additives for providing both high conductivity of the formed film and strong adhesion to the substrates. It can be used for a variety of substrates including glass, PET, PMMA, PC, PI, PEI, etc.
Catalog Number: NovaWire-Ag-SP
Sheet resistance of formed film: 50-100ohm/square
Transparency of formed silver nanowire film: ~95%
Haze: <4%
Curing temperature: ~150 °C for ~15 min
Viscosity: 4000 to 25000mPa.s
Coating and printing methods: screen printing, roller coating etc.
Screen size: ~300 mesh, 55 micron thick
Storage: 3 to 35 degree Celsius
Shake well before use. No sonication.
APPLICATIONS
- Touch screens for smartphones, tablets, and wearable electronics
- Solar cells, solar panels, thin film photovoltaics
- Light-emitting diodes (LEDs), OLED devices, OLED lighting
- Liquid crystal displays
- Flexible displays
- e-paper
- Fillers for high performance conductive adhesives
- Surface enhanced spectroscopy (SERS)
- Sensors and detectors
- Air and water purification
- Medical imaging
- Antimicrobial applications (e.g., bandages, coatings for medical devices, antibacterial fabrics)
- Catalysts
- EMI shielding films and paints
- Optical limiters
- Flexible antennas
- Waveguides
- Compact logic gates
REFERENCES
- Duc Anh Dinh, Kwun Nam Hui, Kwan San Hui, Pushpendra Kumar, Jai Singh, “Silver Nanowires: A Promising Transparent Conducting Electrode Material for Optoelectronic and Electronic Applications”, Reviews in Advanced Sciences and Engineering, 2013, Vol 2, 1–22.
- Yuan-Jun Song, Jing Chen, Jing-Yuan Wu, and Tong Zhang, “Applications of Silver Nanowires on Transparent Conducting Film and Electrode of Electrochemical Capacitor”, Journal of Nanomaterials, 2014, Vol 2014, Article ID 193201, 7 pages.
- Hui-Wang Cui, Katsuaki Suganuma, Hiroshi Uchid, “Highly Stretchable, Electrically Conductive Textiles Fabricated from Silver Nanowires and Cupro Fabrics Using a Simple Dipping-Drying Method”, Nano Research, DOI 10.1007/s12274-014-0649-y.
- Cai-Hong Liu and Xun Yu, “Silver nanowire-based transparent, flexible, and conductive thin film”, Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6(1), 75.
- Feng Xu, Yong Zhu, “Highly Conductive and Stretchable Silver Nanowire Conductors”, Advanced Materials, 2012, Vol 24, Issue 37, 5117–5122.
- Cheng Y, Wang R, Sun J, Gao L, “Highly Conductive and Ultrastretchable Electric Circuits from Covered Yarns and Silver Nanowires”, ACS Nano, 2015, Mar 30.
- Jingjing Ma, Mao-Sheng Zhan, Kai Wang, “Ultralightweight Silver Nanowires Hybrid Polyimide Composite Foams for High-Performance Electromagnetic Interference Shielding”, ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces , 12/2014; 7(1), DOI: 10.1021/am5067095.
- Amjadi M; Pichitpajongkit A; Lee S; Ryu S; Park I, “Highly Stretchable and Sensitive Strain Sensor Based on Silver Nanowire–Elastomer Nanocomposite”, ACS Nano., 2014, 8(5), 5154-63.
- Tate C. Hauger, S. M. Ibrahim Al-Rafia, and Jillian M. Buriak, “Rolling Silver Nanowire Electrodes: Simultaneously Addressing Adhesion, Roughness, and Conductivity”, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2013, 5 (23), 12663–12671.
- Ki-Hun Ok, Jiwan Kim, So-Ra Park, Youngmin Kim, Chan-Jae Lee, Sung-Jei Hong, Min-Gi Kwak, Namsu Kim, Chul Jong Han & Jong-Woong Kim, “Ultra-thin and smooth transparent electrode for flexible and leakage-free organic light-emitting diodes”, Scientific Reports 5, Article number: 9464.
- Weina He, Guangyong Li, Shangquan Zhang, Yong Wei, Jin Wang, Qingwen Li, Xuetong Zhang, “Polypyrrole/Silver Coaxial Nanowire Aero-Sponges for Temperature-Independent Stress Sensing and Stress-Triggered Joule Heating”, ACS Nano, Article ASAP, DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.5b00626, Publication Date (Web): March 26, 2015.
- H. Al-Saleh, G.A. Gelves, U. Sundarara, “Novel Metal Nanowire/Polymer Nanocomposites for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding”, NSTI-Nanotech, 2009, Vol. 2, 505.
- Shanshan Yao and Yong Zhu, “Wearable multifunctional sensors using printed stretchable conductors made of silver nanowires”, Nanoscale, 2014, 6, 2345.
- Ruo-Zhou Li, Anming Hu, Tong Zhang, and Ken D. Oakes, “Direct Writing on Paper of Foldable Capacitive Touch Pads with Silver Nanowire Inks”, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2014, 6 (23), pp 21721–21729
- Adam K. Wanekaya, Wilfred Chen, Nosang V. Myung, Ashok Mulchandani, “Nanowire-Based Electrochemical Biosensors”, Electroanalysis, 2006, 18, No. 6, 533–550.
- Yat Li, Fang Qian, Jie Xiang, Charles M. Lieber, “Nanowire electronic and optoelectronic devices”, Materials Today, Volume 9, Issue 10, October 2006, Pages 18–27.
SYNONYM
Silver nanowires, silver nanofibers, silver, Ag nanowires, Ag nanofibers, Ag, metallic nanowires, metallic nanofibers, conductive nanowires, conductive nanofibers, conductive inks, conductive pastes, silver nanowire, silver nanofiber, Ag nanowire, Ag nanofiber, metallic nanowire, metallic nanofiber, conductive nanowire, conductive nanofiber, conductive ink, conductive paste
SDS